The National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET-UG 2025) is a crucial examination for medical aspirants in India. Understanding the entire NEET UG biology syllabus 2025 and its distribution is essential for effective preparation. Biology holds significant importance in the exam, as it covers 50% of the total weightage, making it a key subject for securing a high score.
This article provides a detailed overview of the NEET UG 2025 Biology syllabus and subject-wise weightage, categorized into Class 11 and Class 12 topics. It also offers strategies to help you plan and optimize your preparation effectively.
Contents
For Class 11 & 12
Following is the Biology syllabus for class 11 and 12. Let’s have a look.
Class 11
The Class 11 syllabus lays down the basic ideas of biology. The essential units are:
| Unit | Chapters |
| Diversity of the Living World | – The Living World – Biological Classification – Plant Kingdom – Animal Kingdom |
| Structural Organisation in Animals and Plants | – Morphology of Flowering Plants – Anatomy of Flowering Plants – Structural Organisation in Animals |
| Cell Structure and Function | – Cell The Unit of Life – Biomolecules – Cell Cycle and Cell Division |
| Plant Physiology | – Transport in Plants – Mineral Nutrition – Photosynthesis in Higher Plants – Respiration in Plants – Plant Growth and Development |
| Human Physiology | – Digestion and Absorption – Breathing and Exchange of Gases – Body Fluids and Circulation – Excretory Products and Their Elimination – Locomotion and Movement – Neural Control and Coordination – Chemical Coordination and Integration |
Class 12
The Class 12 syllabus includes advanced biological concepts required for medical education. The main units are:
| Unit | Chapters |
| Reproduction | – Reproduction in Organisms – Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants – Human Reproduction – Reproductive Health |
| Genetics and Evolution | – Principles of Inheritance and Variation – Molecular Basis of Inheritance – Evolution |
| Biology and Human Welfare | – Human Health and Disease – Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production – Microbes in Human Welfare |
| Biotechnology | – Biotechnology Principles and Processes – Biotechnology and Its Applications |
| Ecology and Environment | – Organisms and Populations – Ecosystem – Biodiversity and Conservation – Environmental Issues |
Unit-Wise Weightage
The biology section of NEET UG 2025 aggregates to 360 marks (90 questions) in the entire 720 marks. The estimated weightage for class 11 goes by the previous trends:-
| Class 11 Units | Weightage (%) | Key Topics | Notes |
| Diversity of the Living World | 12-15 | Plant & Animal Kingdom, classification, biodiversity | Includes classification details for all kingdoms; prepare illustrative examples thoroughly. |
| Structural Organisation in Animals/Plants | 8-10 | Morphology, anatomy, tissues | Detailed diagrams of tissue sections are highly beneficial for scoring in image-based MCQs. |
| Cell Structure and Function | 10-12 | Biomolecules, Cell cycle, organelles | Focus on biomolecule properties and enzyme actions; cell diagrams help. |
| Plant Physiology | 8-10 | Photosynthesis, respiration, growth regulation | Frequently tested mechanisms like chemiosmotic theory; revise formulas for pathways. |
| Human Physiology | 15-18 | Circulation, Neural and Chemical coordination | Prioritize cardiovascular and excretory systems; common for clinical-based scenario MCQs. |
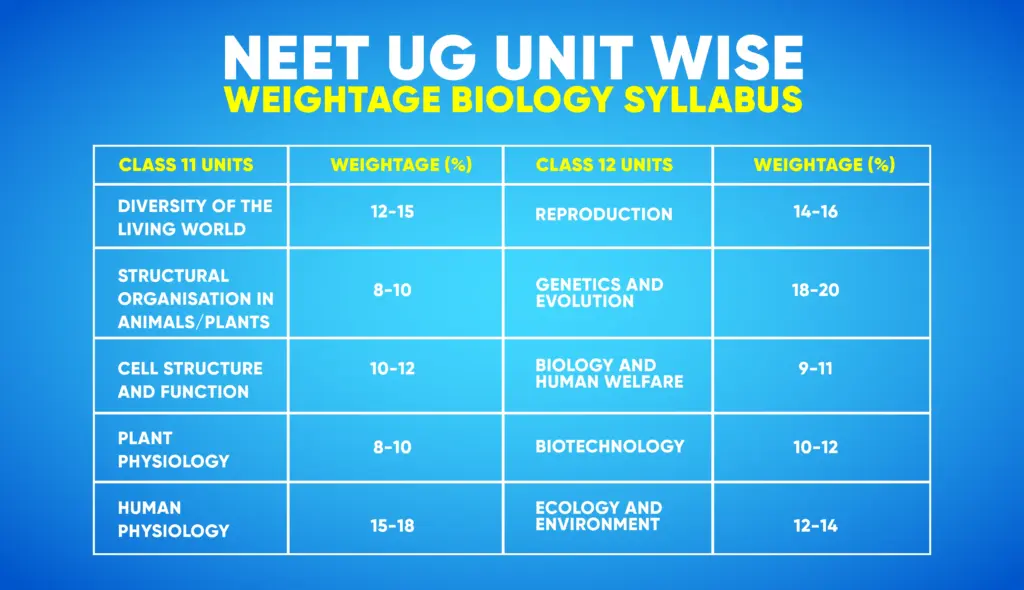
The estimated weightage for class 12 are as following:
| Class 12 Units | Weightage (%) | Key Topics | Notes |
| Reproduction | 14-16 | Human reproduction, sexual reproduction in plants | Understand hormonal regulation and developmental sequences in plants and humans. |
| Genetics and Evolution | 18-20 | Inheritance, gene expression, Hardy-Weinberg | Numerical problems on genetics are common; evolution concepts often tie into population bio. |
| Biology and Human Welfare | 9-11 | Health, diseases, microbes | Study examples like vaccine roles and pathogen classifications; cross-link with immunology. |
| Biotechnology | 10-12 | Genetic engineering, applications | Focus on the methodologies and applications of recombinant DNA technologies. |
| Ecology and Environment | 12-14 | Ecosystem, biodiversity conservation | Prepare from ecological interactions with illustrative case studies and diagrams. |
Topic-Wise Syllabus
Here is the NEET UG Biology syllabus topic-wise for class 11 and 12, covering a comprehensive range of topics essential for medical aspirants.
Class 11
- What is living?; Biodiversity; Need for classification; Taxonomy & Systematics.
- Concept of species and taxonomic hierarchy; Binomial nomenclature.
- Five kingdom classification; Salient features and classification of Monera, Protista, Fungi, Lichens; Viruses and Viroids.
- Salient features and classification of plants into major groups: Algae, Bryophytes, Pteridophytes, Gymnosperms (three to five salient and distinguishing features and at least two examples of each category).
- Salient features and classification of animals: Non-chordates up to phyla level and chordates up to class level (three to five salient features and at least two examples).
Unit 2: Structural Organisation in Animals and Plants
- Morphology and modifications; Tissues.
- Anatomy and functions of different parts of flowering plants: Root, stem, leaf, inflorescence (cymose and racemose), flower, fruit, and seed.
- Families: Malvaceae, Cruciferae, Leguminosae, Compositae, Gramineae (to be dealt with along relevant practicals).
- Animal tissues; Morphology, anatomy and functions of different systems (digestive, circulatory, respiratory, nervous and reproductive) of an insect (frog).
Unit 3: Cell Structure and Function
- Cell theory and cell as the basic unit of life; Structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Plant and animal cells; Cell envelope, cell membrane, cell wall; Cell organelles (endomembrane system, mitochondria, plastids, etc.); Cytoskeleton, cilia, flagella, centrioles.
- Nucleus: Nuclear membrane, chromatin, nucleolus.
- Biomolecules: Structure and function of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids.
- Enzymes: Types, properties, enzyme action, classification and nomenclature.
- Cell division: Cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis and their significance.
Unit 4: Plant Physiology
- Photosynthesis: Autotrophic nutrition, pigments, photochemical and biosynthetic phases, pathways (C3 and C4), factors.
- Respiration: Glycolysis, TCA cycle, ETC, ATP generation, respiratory quotient.
- Plant growth and development: Growth phases, growth rate, differentiation, growth regulators (auxin, cytokinin, gibberellin, ethylene, ABA).
Unit 5: Human Physiology
- Breathing and Respiration: Mechanism, regulation, volumes, disorders.
- Body fluids and circulation: Human circulatory system, cardiac cycle, ECG, disorders (hypertension, coronary artery disease).
- Excretion: Modes of excretion, human excretory system, osmoregulation.
- Locomotion and movement: Types, muscle contraction, skeletal system, disorders (arthritis, gout).
- Neural control and coordination: Nervous system, nerve impulse conduction.
- Chemical coordination and regulation: Human endocrine system, hormones, disorders.
Class 12
Unit 6: Reproduction
- Sexual reproduction in flowering plants: Flower structure, gametophyte development, pollination, fertilization, post-fertilization events, apomixis.
- Human reproduction: Systems, gametogenesis, menstrual cycle, embryo development, implantation, parturition, lactation.
- Reproductive health: STD prevention, contraception, infertility treatments (IVF, ZIFT, GIFT).
Unit 7: Genetics and Evolution
- Heredity and variation: Mendel’s laws, deviations, chromosomal theory, sex determination, disorders (Down’s syndrome, hemophilia).
- Molecular basis: DNA structure, replication, transcription, translation, operon model, genetic fingerprinting.
- Evolution: Origin, evidence, Hardy-Weinberg principle, human evolution.
Unit 8: Biology and Human Welfare
- Health and diseases: Pathogens, human diseases (malaria, dengue), immunity, vaccines.
- Microbes: Household/industrial uses, sewage treatment, energy generation, biofertilizers.
Unit 9: Biotechnology and Its Applications
- Genetic engineering (recombinant DNA technology).
- Applications: GMOs, gene therapy, vaccines, biopiracy.
Unit 10: Ecology and Environment
- Organisms and environment: Populations, interactions, age distribution.
- Ecosystem: Energy flow, biodiversity conservation, hotspots.
Strategies for Biology Preparation
Here are a few strategies for NEET UG Biology preparation:
- Know the Weightage: Major focus on high-weightage topics such as Genetics, Ecology and Human Physiology etc.
- NCERT First: Read them thoroughly with clarity and breadth of concept.
- Practice Regularly: Previous year papers and mock tests would be your best friends for sure.
- Make Notes: Points to remember-Highlight the key, make a quick revision of notes.
- Review Often: Review the previously read material while reading new material to retain it.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
Which chapters in Biology should I focus on to score high in NEET UG 2025?
To score well, prioritize high-weightage topics like Human Physiology, Plant Physiology, Reproduction, Ecology, and Genetics. These areas are not only crucial for understanding biological processes but are also frequently tested in the exam.
How are the questions distributed across Botany and Zoology?
The distribution is typically balanced, with Botany and Zoology each contributing 50% to the Biology section. In practice, around 45–50 questions are asked from Botany and an equal number from Zoology, giving a total of 90 questions for Biology.
Which topics in Botany carry the highest weightage for NEET UG 2025?
In Botany, high-weightage topics include Plant Physiology, Cell Biology, Plant Diversity, Reproduction in Plants and Ecology and Environment. These areas are typically asked frequently and cover a significant portion of the Botany section.
What is the weightage of Zoology in NEET UG 2025?
Zoology carries about 50% of the Biology section’s weightage, which translates to around 180 marks. The most important topics include Human Physiology, Reproduction in Humans, Genetics and Evolution and Human Health and Disease.

